Getting Started
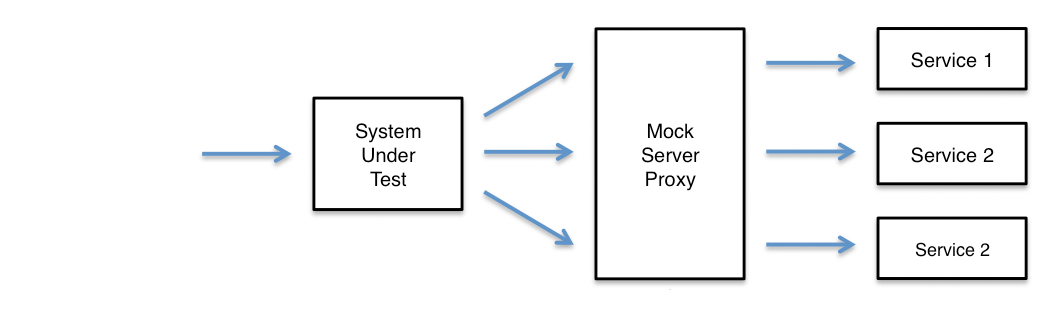
To use MockServer Proxy to analysis an existing system:
- Start MockServer Proxy
- Configure Clients
- Run Scenarios
- Analyse Behaviour
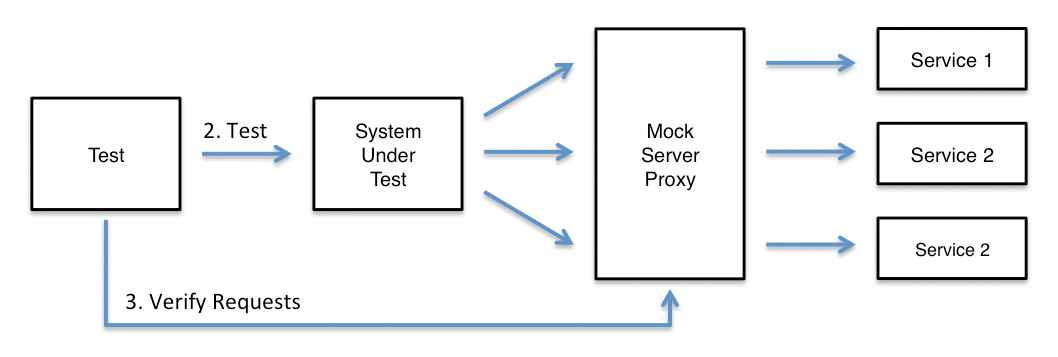
To use MockServer Proxy to verify requests:
- Start MockServer Proxy
- Configure Clients
- Run Test Scenarios
- Verify Requests
0. Start MockServer
MockServer is flexible and support numerous usage patterns.
The MockServer and MockServer Proxy can be run:
- via a Maven Plugin as part of a Maven build cycle
- programmatically via a Java API in an @Before or @After method
- using a JUnit @Rule via a @Rule annotated field in a JUnit test
- from the command line as a stand-alone process in a test environment
- as a deployable WAR to an existing application server
- as a Node.js (npm) module from any Node.js code
- as a Grunt plugin as part of a Grunt build cycle
- as a Docker container in any Docker enabled environment
MockServer and MockServer Proxy is available as:
- a stand alone Netty web server that is fully self contained
- a deployable WAR that runs on any JEE web server
- a maven plugin
- an npm plugin
- a Grunt plugin
- a fully encapsulated Docker container
- a Homebrew package
It is also possible to build and run MockServer directly from source code
To simplify configuration all MockServer versions (except the deployable WAR) only use a single port to support HTTP, HTTPS and SOCKS. This is achieved by dynamically detecting if the client is using HTTP, HTTPS or SOCKS.
Start MockServer Proxy
If the proxy is being started programmatically from within the same JVM using org.mockserver.proxy.ProxyRunner or org.mockserver.integration.ClientAndProxy then the environment variables "http.proxyHost" and "http.proxyPort" will be set automatically.
If the proxy is being started as separate JVM, for example using the command line, then the system being analysed needs the following command line options to set the correct environment variables.
-Dhttp.proxyHost=<proxy hostname> -Dhttp.proxyPort=<proxy port>For example:
-DproxySet=true -Dhttp.proxyHost=localhost -Dhttp.proxyPort=10902. Configure Clients
The page on configuring clients gives full details and example code on how to configure the system being analysed.
3. Analysing Behaviour
To analyse the requests that a system makes the proxy can be used to record all requests and their corresponding responses.
Retrieve Recorded Requests
Recorded requests can be retrieved as a list of requests received by the proxy in either JSON or Java code.
HttpRequest[] recordedRequests = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedRequests(
request()
);var proxyClient = require('mockserver-client').proxyClient;
proxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedRequests({})
.then(
function (recordedRequests) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(recordedRequests));
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=REQUESTS"HttpRequest[] recordedRequests = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedRequests(
request()
.withPath("/some/path")
.withMethod("POST")
);var proxyClient = require('mockserver-client').proxyClient;
proxyClient("localhost", 1090).retrieveRecordedRequests({
"path": "/some/path",
"method": "POST"
}).then(
function (recordedRequests) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(recordedRequests));
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=REQUESTS" -d '{
"path": "/some/path",
"method": "POST"
}'String recordedRequests = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedRequests(
request()
.withPath("/some/path")
.withMethod("POST"),
Format.JAVA
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=REQUESTS&format=JAVA" -d '{
"path": "/some/path"
}'String recordedRequests = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedRequests(
request()
.withPath("/some/path")
.withMethod("POST"),
Format.JSON
);var proxyClient = require('mockserver-client').proxyClient;
proxyClient("localhost", 1090).retrieveRecordedRequests({
"path": "/some/path",
"method": "POST"
}).then(
function (recordedRequests) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(recordedRequests));
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=REQUESTS&format=JSON" -d '{
"path": "/some/path"
}'Retrieve Recorded Expectations
Recorded requests-response pairs can be retrieved as a list of expectations containing the request and response that was proxied in either JSON or Java code.
The list of retrieved expectations can be used to setup expectations in MockServer to support mocking.
Expectation[] recordedExpectations = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedExpectations(
request()
);var proxyClient = require('mockserver-client').proxyClient;
proxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedExpectations({})
.then(
function (recordedExpectations) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(recordedExpectations));
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=RECORDED_EXPECTATIONS"Expectation[] recordedExpectations = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedExpectations(
request()
.withPath("/some/path")
.withMethod("POST")
);var proxyClient = require('mockserver-client').proxyClient;
proxyClient("localhost", 1090).retrieveRecordedExpectations({
"path": "/some/path",
"method": "POST"
}).then(
function (recordedExpectations) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(recordedExpectations));
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=RECORDED_EXPECTATIONS" -d '{
"path": "/some/path",
"method": "POST"
}'String recordedExpectations = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedExpectations(
request()
.withPath("/some/path")
.withMethod("POST"),
Format.JAVA
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=RECORDED_EXPECTATIONS&format=JAVA" -d '{
"path": "/some/path"
}'String recordedExpectations = new ProxyClient("localhost", 1090)
.retrieveRecordedExpectations(
request()
.withPath("/some/path")
.withMethod("POST"),
Format.JSON
);var proxyClient = require('mockserver-client').proxyClient;
proxyClient("localhost", 1090).retrieveRecordedExpectations({
"path": "/some/path",
"method": "POST"
}).then(
function (recordedExpectations) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(recordedExpectations));
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1090/retrieve?type=RECORDED_EXPECTATIONS&format=JSON" -d '{
"path": "/some/path"
}'3. Verify Requests
The MockServer allows the verification of requests by specifying:
- a request matcher and a count indicating the number of times the request should be matched
- a sequence of request matchers that is matched in order
Verifying Repeating Requests
Verify that a request has been received by MockServer a specific number of times using a Verification
new MockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
request()
.withPath("/some/path"),
VerificationTimes.atLeast(2)
);var mockServerClient = require('mockserver-client').mockServerClient;
mockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
{
'path': '/some/path'
}, 2, false)
.then(
function () {
console.log("request found exactly 2 times");
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1080/verify" -d '{
"httpRequest": {
"path": "/simple"
},
"times": {
"count": 2,
"exact": false
}
}'new MockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
request()
.withPath("/some/path"),
VerificationTimes.once()
);var mockServerClient = require('mockserver-client').mockServerClient;
mockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
{
'path': '/some/path'
}, 1, true)
.then(
function () {
console.log("request found exactly 2 times");
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1080/verify" -d '{
"httpRequest": {
"path": "/simple"
},
"times": {
"count": 1,
"exact": true
}
}'new MockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
request()
.withPath("/some/path"),
VerificationTimes.exactly(0)
);var mockServerClient = require('mockserver-client').mockServerClient;
mockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
{
'path': '/some/path'
}, 0, true)
.then(
function () {
console.log("request found exactly 2 times");
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1080/verify" -d '{
"httpRequest": {
"path": "/simple"
},
"times": {
"count": 0,
"exact": true
}
}'Verifying Request Sequences
Verify that a sequence of requests has been received by MockServer in the specified order using a VerificationSequence
The each request in the sequence will be verified to have been received at least once, in the exact order specified.
new MockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verify(
request()
.withPath("/some/path/one"),
request()
.withPath("/some/path/two"),
request()
.withPath("/some/path/three")
);var mockServerClient = require('mockserver-client').mockServerClient;
mockServerClient("localhost", 1080)
.verifySequence(
{
'path': '/some/path/one'
},
{
'path': '/some/path/two'
},
{
'path': '/some/path/three'
}
)
.then(
function () {
console.log("request sequence found in the order specified");
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1080/verifySequence" -d '[
{
"path": "/some/path/one"
},
{
"path": "/some/path/two"
},
{
"path": "/some/path/three"
}
]'