Isolate Single Service
During deployment and debugging it can be helpful to run a single application or service or handle a sub-set of requests on a local machine in debug mode. Using MockServer it is easy to selectively forward requests to a local process running in debug mode, all other request can be forwarded to the real services for example running in a QA or UAT environment.
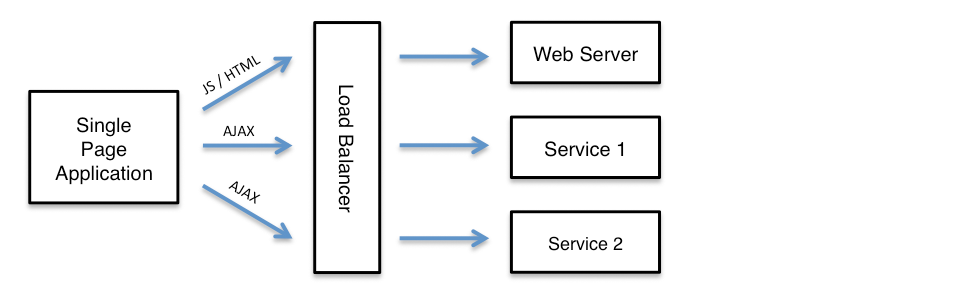
For example a single page application may load static resources such as HTML, CSS and JavaScript from a web server and also make AJAX calls to one or more separate services, as follows:
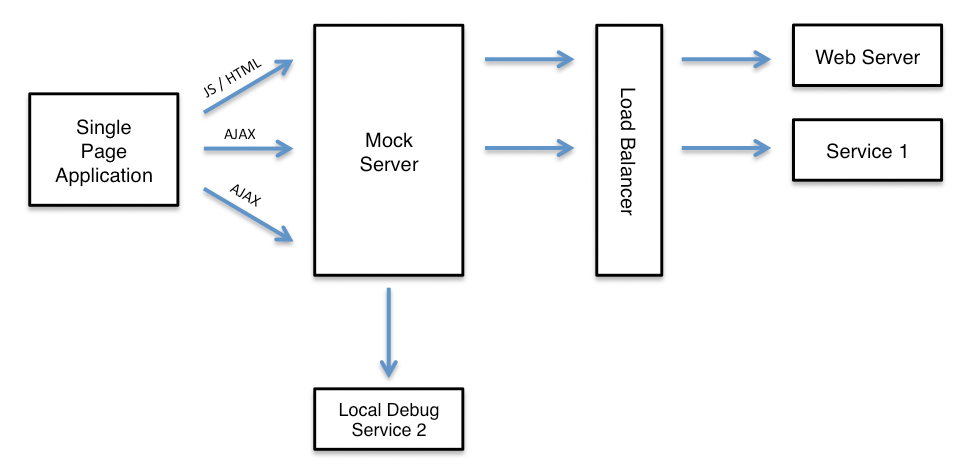
To isolate a single AJAX service, for development or debugging, the MockServer can selectively forward specific requests to a local instance of the service:
One of the simplest ways to do this is using Node.js. In the example below all requests matching path "/rest.*" (i.e. starting with /rest) will go to the local machine on port 8080 whereas all other requests will go to a remote machine (i.e. a load balancer or remote server) on ip 192.168.50.10 and port 443.
First create a package.json file as follows:
{
"name": "mockserver_as_reverse_proxy",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "server.js",
"dependencies": {
"mockserver-node": "5.3.0",
"mockserver-client": "5.3.0"
}
}<Then create the server.js file that starts MockServer and sets up the forwarding rules as different expectations, as follows:
var mockserver = require('mockserver-node');
var mockServerClient = require('mockserver-client').mockServerClient;
var HTTP_PORT = 1080;
mockserver
.start_mockserver({
serverPort: HTTP_PORT
})
.then(function () {
// forward backend REST API request to local machine
mockServerClient("localhost", HTTP_PORT)
.mockAnyResponse({
"httpRequest": {
"path": "/rest.*"
},
"httpForward": { // local machine Tomcat instance
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 8080,
"scheme": "HTTP"
},
"times": {
"unlimited": true
}
})
.then(
function () {
// forward all other request to QA environment
mockServerClient("localhost", HTTP_PORT)
.mockAnyResponse({
"httpRequest": {
"path": "/.*"
},
"httpForward": { // QA environment load balancer
"host": "192.168.50.10",
"port": 443,
"scheme": "HTTPS"
},
"times": {
"unlimited": true
}
})
.then(
function () {
console.log("created expectations");
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
);
});
console.log("started on port: " + HTTP_PORT);
// stop MockServer if Node exist abnormally
process.on('uncaughtException', function (err) {
console.log('uncaught exception - stopping node server: ' + JSON.stringify(err));
mockserver.stop_mockserver();
throw err;
});
// stop MockServer if Node exits normally
process.on('exit', function () {
console.log('exit - stopping node server');
mockserver.stop_mockserver();
});
// stop MockServer when Ctrl-C is used
process.on('SIGINT', function () {
console.log('SIGINT - stopping node server');
mockserver.stop_mockserver();
process.exit(0);
});
// stop MockServer when a kill shell command is used
process.on('SIGTERM', function () {
console.log('SIGTERM - stopping node server');
mockserver.stop_mockserver();
process.exit(0);
});To start the process install the npm module and launch Node.js, as follows:
npm i
node server.js